Potential Energy of a Spring
Potential Energy of a Spring: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Work Done by Spring Force, Conservative and Non-conservative Forces and Graph of Potential Energy.
Important Questions on Potential Energy of a Spring
Which of the following forces is not conservative?
In a gravitational force field a particle is taken from to along different paths as shown in figure. Then
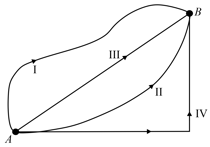
Which of the following statement is not true?
The potential energy of a system increases if work is done
Write three different statements for defining a conservative force.
Example of a non-conservative force is:
A curved surface is shown in figure. The portion is frictionless. There are two spherical balls of identical radii and masses, balls are released from rest one by one from which is at a slightly greater height than . With the surface , ball has a small friction and ball has a negligible friction. For which balls is total mechanical energy conserved?
Identify the false statement from the following.
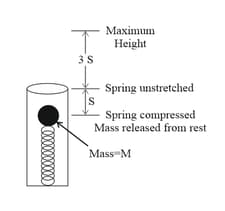
A spring-loaded toy gun is used to shoot a ball of mass M straight up in the air. The ball is not attached to the spring. The ball is pushed down onto the spring so that the spring is compressed a distance S below its un-stretched point. After release, the ball reaches a maximum height 3S, measured from the un-stretched position of the spring (see diagram). The spring constant of the spring is:-
Two wires are stretched through same distance. The force constant of second wire is half as that of the first wire. The ratio of work done to stretch first wire and second wire will be
A block of mass 0.18 kg is attached to a spring of force constant . The coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0.1. Initially the block is at rest and the spring is unstretched. An impulse is given to the block.
The block slides a distance of 0.06m and comes to rest for the first time the initial velocity of the block in is . Then N is
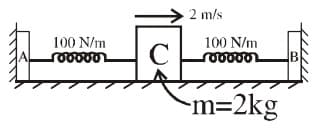
and are massless supports attached to two springs, both the springs are identical and light. Friction coefficient between block and horizontal surface is . When both the springs are in their natural length block was given a velocity of towards right. Then the distance travelled by block before coming to rest for the first time is :
The block of mass moving on the frictionless horizontal surface collides with the spring of spring constant and compresses it by length . The maximum momentum of the block after collision is
The elastic potential energy of a stretched spring is given by where is the displacement in meter and is in joule, then the force constant of the spring is
Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants and , such that . They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then by the same force (case b). the work done by the springs and are related as, in case
Assertion: When a spring is elongated work done by spring is negative but when it compressed work done by spring is positive.
Reason: Work done by spring is path independent.
Assertion: When a spring is elongated work done by spring is negative but when it compressed work done by spring is positive.
Reason: Work done by spring is path independent.
A knife of mass slides on a frictionless wedge of mass between two frictionless guides. At the instant shown in figure, the spring has initial compression . Ground is also frictionless. Velocity of wedge when knife is about to touch the ground is (assume spring is ideal for large compressions) -
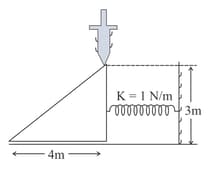
A spring of force constant has initial stretch 0.2 m. In changing the stretch to 0.25 m, the increase of PE is about-
Two springs have their force constant as and . When they are stretched by the same force
